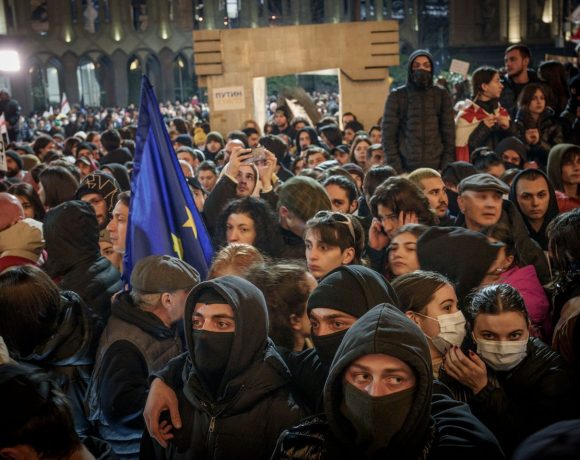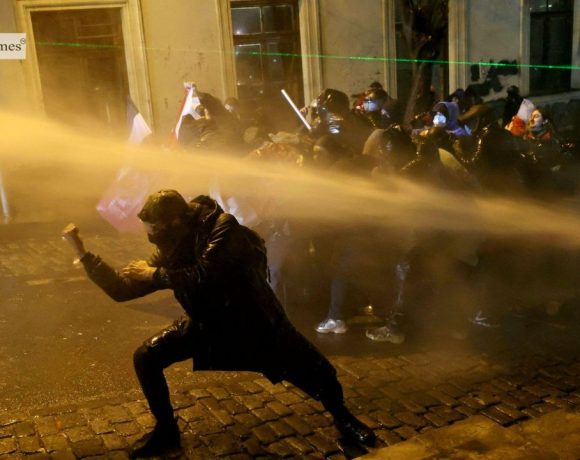
A BBC investigation suggests that Georgian authorities used a World War One–era chemical agent, known as camite, in water cannons during anti-government protests in late 2024. Demonstrators in Tbilisi reported severe burning sensations, difficulty breathing, coughing and vomiting—symptoms that persisted for weeks. Doctors, chemical weapons specialists, and whistleblowers from Georgia’s riot police provided evidence pointing toward the use of this long-discontinued compound, once deployed by France in WW1 and eventually abandoned due to its prolonged harmful effects.
Paediatrician and protester Dr Konstantine Chakhunashvili conducted a survey of nearly 350 affected demonstrators, finding that almost half experienced symptoms lasting more than 30 days. His study, soon to be published in Toxicology Reports, also noted abnormal heart electrical activity among many participants. These findings supported theories from journalists, civil rights groups and medical experts that the water cannon contained more than just irritants like pepper spray or CS gas.
Whistleblowers from Georgia’s Special Tasks Department revealed that the chemical used closely resembles one tested in 2009, which they described as extremely difficult to wash off and far more harmful than standard tear gas. Despite recommendations against its use, they say it continued to be loaded into water cannon vehicles for years. The Georgian government dismissed the BBC’s findings as “absurd,” insisting police acted lawfully against what they called “violent criminals.”
Pic Courtesy: google/ images are subject to copyright

